

BENEFITS
How it works:
The active ingredient in Ultimate Glucosamine® brand of N-Acetylglucosamine works to reduce inflammation and to build back essential joint structures. N-Acetylglucosamine reduces pain and inflammation by reducing the amount of an inflammatory enzyme called COX-2. N-Acetylglucosamine does this without the potential side effects associated with regular pain relievers. Moreover, it is complementary to NSAIDs.
References:
How it works:
This was shown in a study with the N-Acetylglucosamine prodrug glucosamine sulphate. In this 3-year study there was no loss of cartilage (as evidenced by joint space narrowing) in the glucosamine treated group but the placebo treated group had a significant loss of cartilage.
References:
How it works:
By nourishing and lubricating joints, Glucosamine aids in enhancing joint function, making daily activities easier and more comfortable. The positive impact of N-Acetylglucosamine on cartilage repair was illustrated in the laboratory setting. N-Acetylglucosamine restored the cartilaginous surface but placebo treatment showed a continued defect in the surface of the cartilage.
References:
How it works:
Ultimate Glucosamine® supports the production of cartilage, which acts as a cushion between bones, providing protection and reducing friction during movement.
How it works:
Ultimate Glucosamine® is known for its ability to support joint health and cartilage function. It helps maintain the structural integrity of joints and promotes better mobility and flexibility. Thus, incorporating Ultimate Glucosamine® into your daily routine can contribute to long-term joint health, supporting active lifestyles and overall well-being as you age.
REAL PEOPLE,
REAL STORIES
Join thousands of people getting lasting relief from Joint Pain with Ultimate Glucosamine®
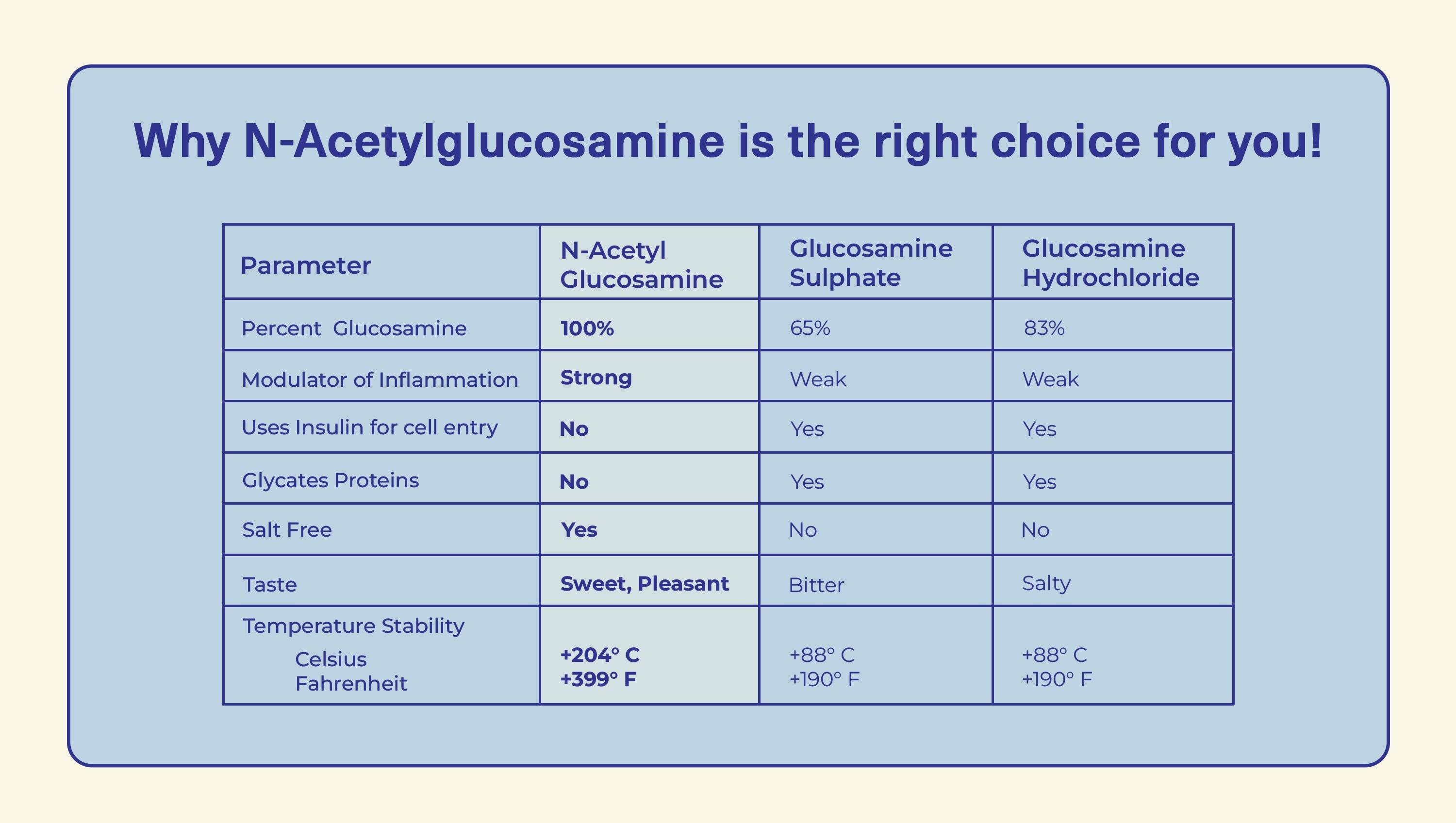
Learn the difference in Glucosamine types:

Biological Advantage of Ultimate Glucosamine®
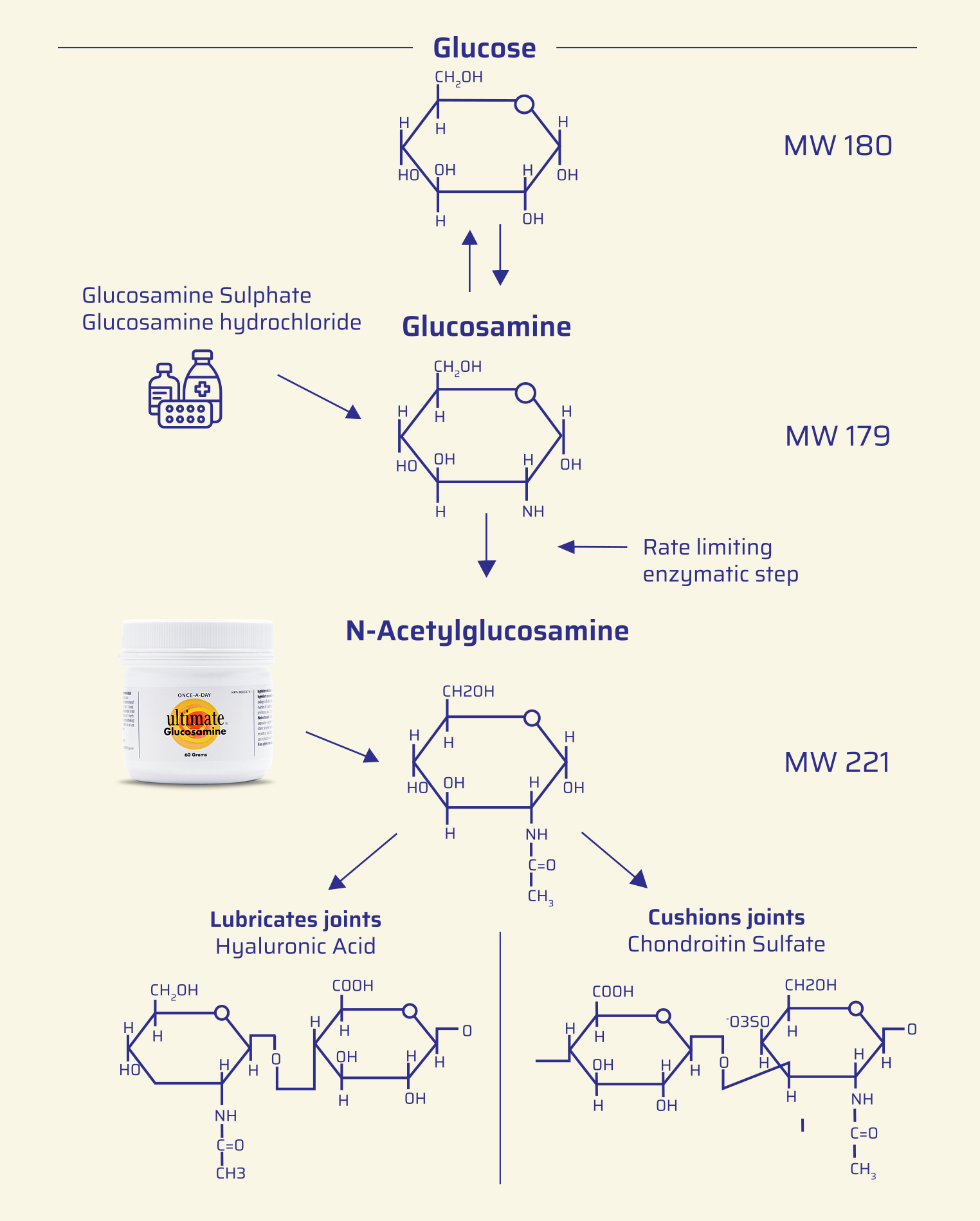
The Biological Advantage of N-Acetylglucosamine chart shows the process by which the human cell makes its own supply of N-Acetylglucosamine to produce hyaluronic acid (lower left) and chondroitin (lower right).
The chart is divided in three columns.
The central column depicts in graphic form the various molecules that are formed on the way to becoming N-Acetylglucosamine. The arrows between the molecules indicate whether the step from one molecule or the other is reversible. A single arrow indicates that the molecular change is not reversible. The left-hand column illustrates where along the pathway the commercially available glucosamine products enter the pathway. The right-hand column shows the size of the molecules in the pathway expressed as the
molecular weight.
What this pathway tells us:
The glucosamine sulphate or hydrochloride must first be converted to N-Acetylglucosamine before it can be made into hyaluronic acid or chondroitin. Note the double arrow between glucose and glucosamine.
Glucosamine can also be converted back to glucose and used for energy which makes it an inefficient treatment.
FAQs
Find the most frequently asked questions below.
















 Afrikaans
Afrikaans Shqip
Shqip አማርኛ
አማርኛ العربية
العربية Հայերեն
Հայերեն Azərbaycan dili
Azərbaycan dili Euskara
Euskara Беларуская мова
Беларуская мова বাংলা
বাংলা Bosanski
Bosanski Български
Български Català
Català Cebuano
Cebuano Chichewa
Chichewa 简体中文
简体中文 繁體中文
繁體中文 Corsu
Corsu Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Esperanto
Esperanto Eesti
Eesti Filipino
Filipino Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Frysk
Frysk Galego
Galego ქართული
ქართული Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી Kreyol ayisyen
Kreyol ayisyen Harshen Hausa
Harshen Hausa Ōlelo Hawaiʻi
Ōlelo Hawaiʻi עִבְרִית
עִבְרִית हिन्दी
हिन्दी Hmong
Hmong Magyar
Magyar Íslenska
Íslenska Igbo
Igbo Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Gaeilge
Gaeilge Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 Basa Jawa
Basa Jawa ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ Қазақ тілі
Қазақ тілі ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ 한국어
한국어 كوردی
كوردی Кыргызча
Кыргызча ພາສາລາວ
ພາສາລາວ Latin
Latin Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch Македонски јазик
Македонски јазик Malagasy
Malagasy Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu മലയാളം
മലയാളം Maltese
Maltese Te Reo Māori
Te Reo Māori मराठी
मराठी Монгол
Монгол ဗမာစာ
ဗမာစာ नेपाली
नेपाली Norsk bokmål
Norsk bokmål پښتو
پښتو فارسی
فارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ Română
Română Русский
Русский Samoan
Samoan Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig Српски језик
Српски језик Sesotho
Sesotho Shona
Shona سنڌي
سنڌي සිංහල
සිංහල Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Afsoomaali
Afsoomaali Español
Español Basa Sunda
Basa Sunda Kiswahili
Kiswahili Svenska
Svenska Тоҷикӣ
Тоҷикӣ தமிழ்
தமிழ் తెలుగు
తెలుగు ไทย
ไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو O‘zbekcha
O‘zbekcha Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Cymraeg
Cymraeg isiXhosa
isiXhosa יידיש
יידיש Yorùbá
Yorùbá Zulu
Zulu